Humanoid Robot Jumping Curve Math Modelling
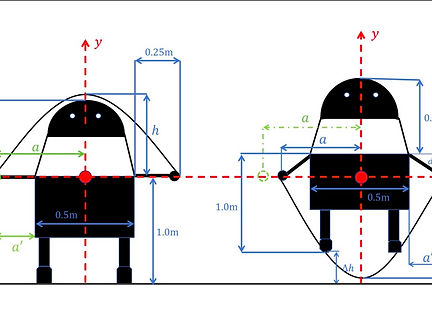
Robot’s Motion on the Ground and in the Air
The robot jumps while its hands stay at a fixed height. As the shoulder rises, the arms rotate from horizontal to oblique, reducing hand distance. This changing geometry directly controls how the rope narrows and swings beneath the robot.
Jumping Height Over Time
Here I model the vertical jumping height as a periodic piecewise function: parabolic flight during the jump and a flat segment on the ground. Matching this timing with one rope revolution per second ensures the robot reliably clears the rope each jump.

Modeling Pipeline
This flow chart shows my modeling process: analyze robot motion, define key parameters, approximate the rope as a catenary, refine it using the Jacobi elliptic function, and finally integrate everything into one function that can be visualized and tested in MATLAB.

3D Rope Trajectory
By plotting the rope’s 2D shape over time, I generate this 3D surface for one full revolution. It visualizes how the rope moves around the robot in space and provides a direct reference for future real-time control of the robot.
Rope as Catenary
When the rope hangs between two hands, it forms a catenary. In rotation, centrifugal force plays the role of “gravity” in the rotation plane, so I can still use the classic catenary equation as the basis of the rope’s shape.
Linear Fit Between
𝐵 and 𝑎
This graph shows how parameter
𝐵 changes with hand distance
𝑎. By sampling many
(𝑎,𝐵) pairs and applying linear regression, I obtain a simple approximate relationship. This makes the final rope trajectory function easier to tune and physically interpret.

2D Rope Shapes at Key Times
These curves show the rope at takeoff, highest point, and landing. At the peak, the rope becomes narrow with maximum vertical span directly under the robot, matching the predicted behavior and confirming that the model captures realistic jump rope motion.
Effect of Longer Arms
Here I increase the arm length and recalculate the rope shapes at three times. The longer arms allow higher jumps and change the rope’s trajectory. This test shows the model can adapt to different humanoid sizes and design choices.